KAUST’s sustainability goals include a commitment to zero water waste, guided by a water management plan that calls for a reduction of the total on-campus consumption of potable water, including any loss from water distribution.


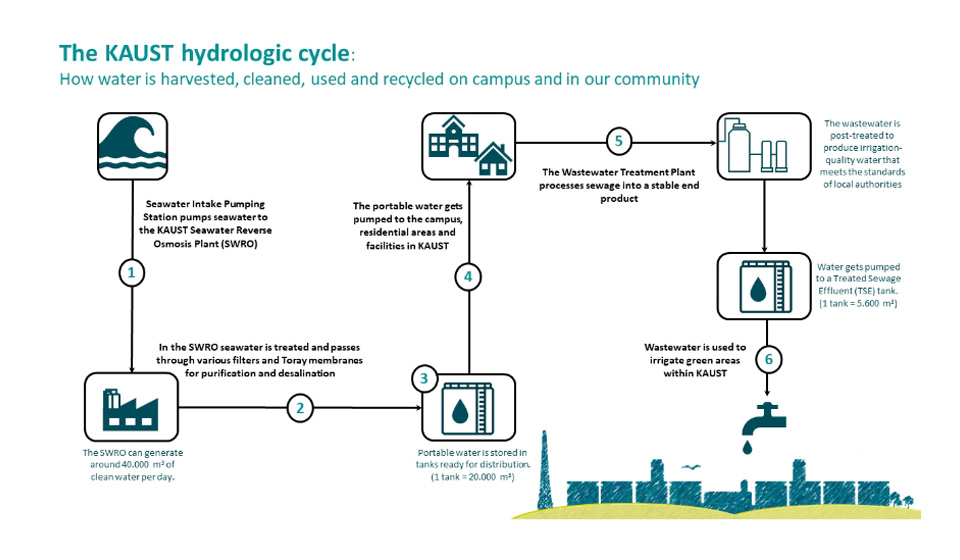
We produce all of our potable water from desalination, collect all of our wastewater for treatment, and reuse all of the resulting treated effluents in landscaping—completing a full water cycle in an effort toward resource circularity.
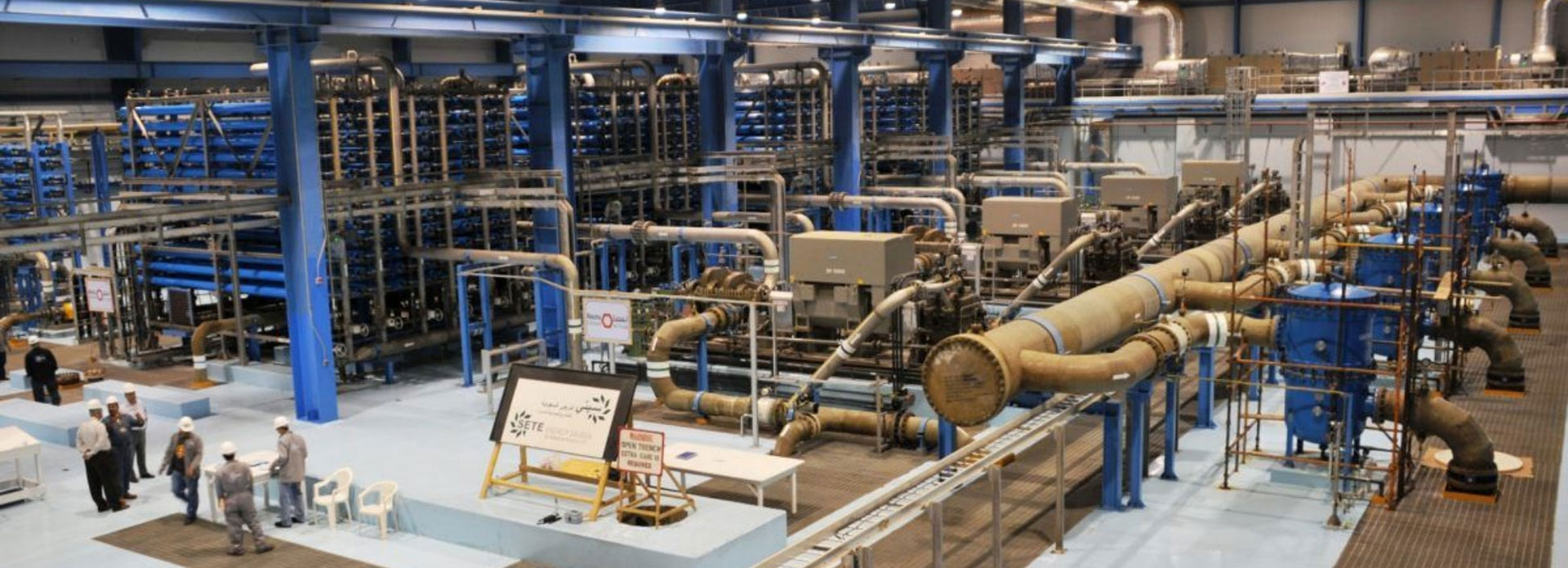

KAUST WATER DESALINATION PLANT
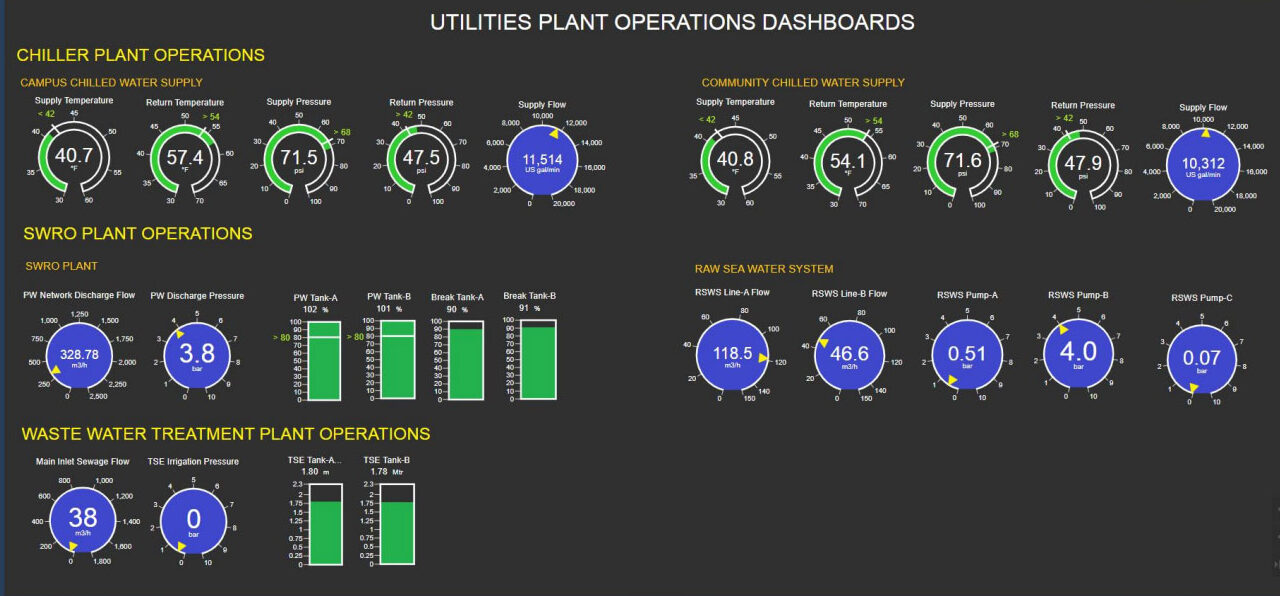
To provide the university and our community with potable water, KAUST owns and operates a Seawater Reverse Osmosis Desalination (SWRO) Plant with a 27,000 m3/day production capacity. This plant produces, monitors, and tracks all potable water provided to all consumers. The water it produces is routinely tested to ensure the highest quality and safety.
In 2019, 147,449 m³ of potable water produced by the plant was used by the KAUST campus. With 4,349 full-time students, faculty, and staff on campus, our estimated water consumption per capita for that year was 34 m³.
WATER USED BY ACADEMIC CAMPUS (m³) x1000
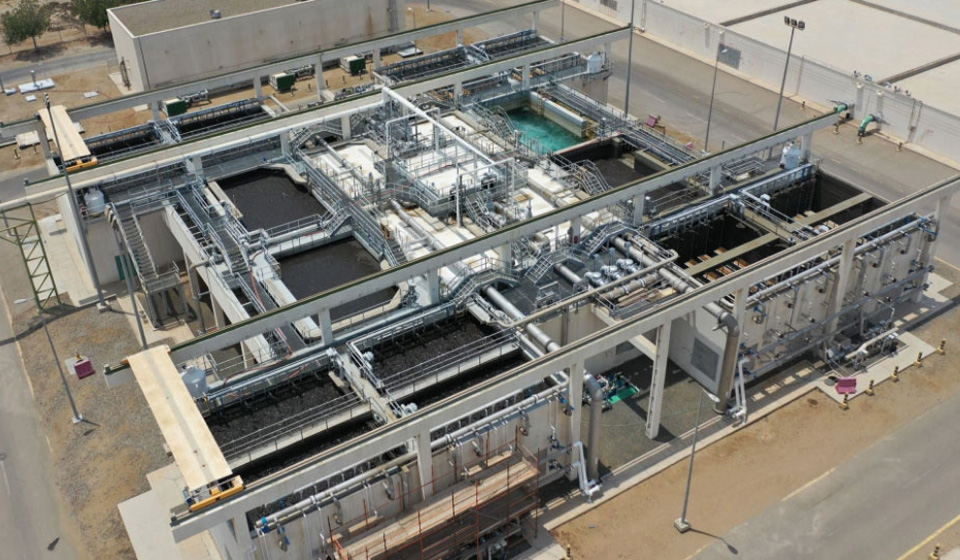
KAUST WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANT
Wastewater—including stormwater, gray water, and black water from KAUST’s campus and the neighboring community—is collected and channeled to our wastewater treatment plant for treatment and reuse as irrigation water. Our Wastewater Management Procedure can be found here.
This state-of-the-art plant can treat 11,500 m³/day of effluent using membrane biological reactor technology. It ensures that the produced treated sewage effluent (TSE) meets rigorous international standards by testing effluents three times a day at an in-house laboratory and once every two weeks at an independent third-party laboratory.
The average amount of TSE produced annually by the plant is 1.6 million m³, with an average daily inlet effluent of 4,500 m³/ day.
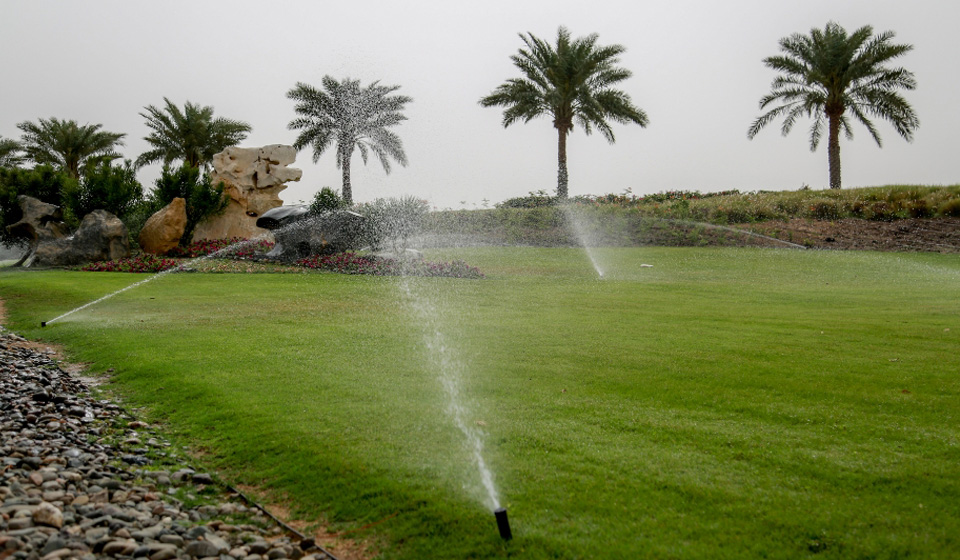
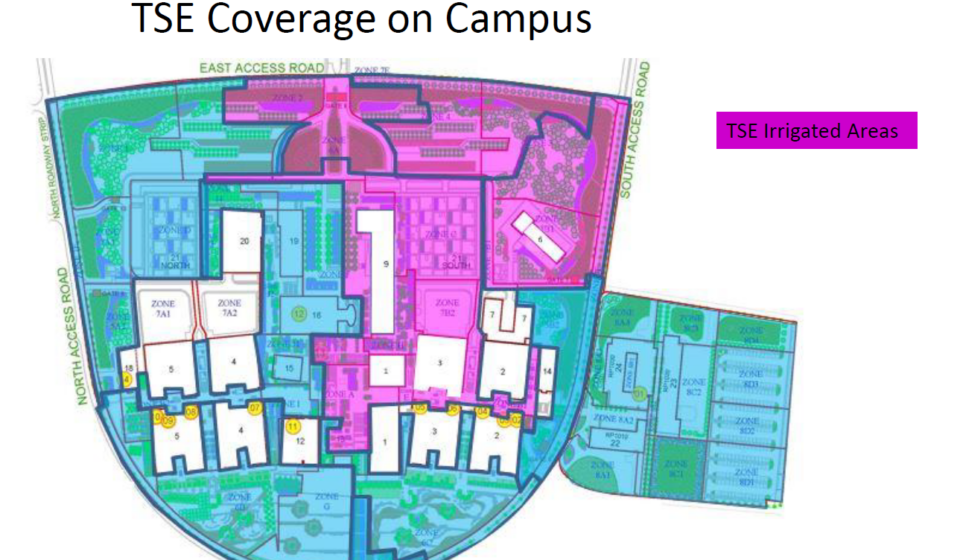
KAUST is proud to reuse 100% of its produced TSE to irrigate green spaces across the academic campus and surrounding community. 35% of the total irrigation water used daily for all landscaping at KAUST comes from TSE, and so does 38% of the daily total irrigation water used for the academic campus.
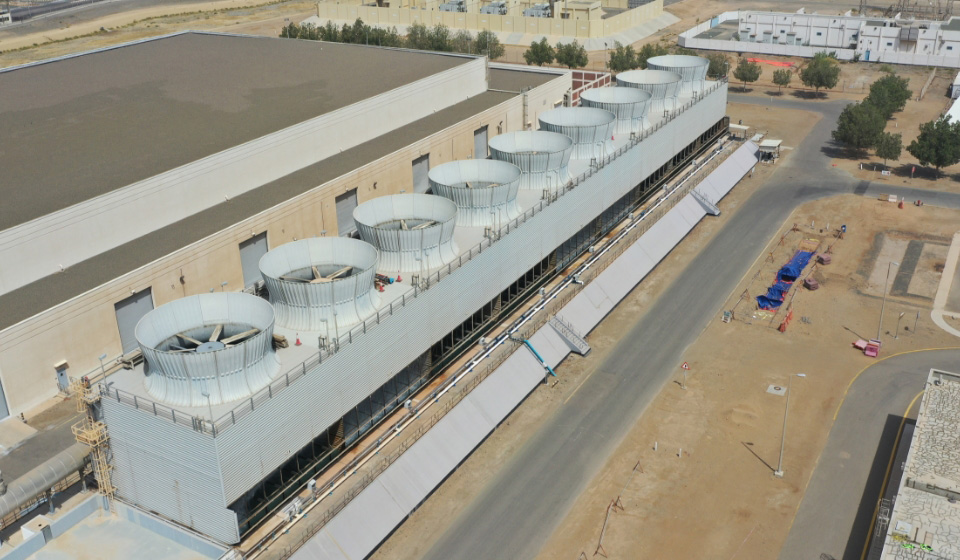
KAUST CENTRAL CHILLED WATER PLANT
Given our local climate, KAUST operates a central chilled water plant designed to produce up to 45,000 tons of refrigerant (TR), with a future expansion capability of an additional 7,000 TR.
Through a 24 km-long network, chilled water is provided to campus buildings, residential apartments, facilities, and central service buildings. The plant is continuously monitored to ensure process optimization and energy efficiency.
WATER SYSTEM POLLUTION PREVENTION
KAUST also carries several actions to prevent water system pollution such as oil spill emergency drills or construction/renovation project reviews.
In addition, KAUST routinely tries to implement efficient and sustainable biological control measures in its water bodies.
WATER-SAVING ACTIONS
EQUIPMENT
All conventional water fixtures across KAUST have been replaced with water-saving devices, reducing water flow by 40% to 55%.
On campus, all faucets have been equipped with touchless automatic motion sensors, for minimal water waste.
Displacement tanks have been installed on all toilets, reducing the volume of water used for each discharge.
WATER REFILLING
STATIONS
To optimize access to drinking water on campus, we have installed free water refill stations (Elkay ezH2O ®️ bottle filling stations). These stations are located in every KAUST building and in the campus diner, encouraging students, faculty, staff, and visitors to bring and use their own bottles, which cuts down on plastic and water waste.
WATER CONSCIOUS LANDSCAPING
To reduce daily irrigation needs, we have implemented xeriscaping design concepts both on campus and in the surrounding residential community, at more than 100 sites.
This xeriscaping, together with the conversion of some of the potable irrigation network to TSE, landscaping optimization, irrigation shut off day, and residential backyard site optimization, has resulted in a 50% reduction in water used for irrigation since 2015.
The preserved landscape comprises a worldwide collection with more than 144 plant species, of which 101 (70%) are drought-tolerant plants, appropriate to the region’s dry environment.





TESTING NEW SUSTAINABLE WATER EXTRACTION TECHNOLOGIES
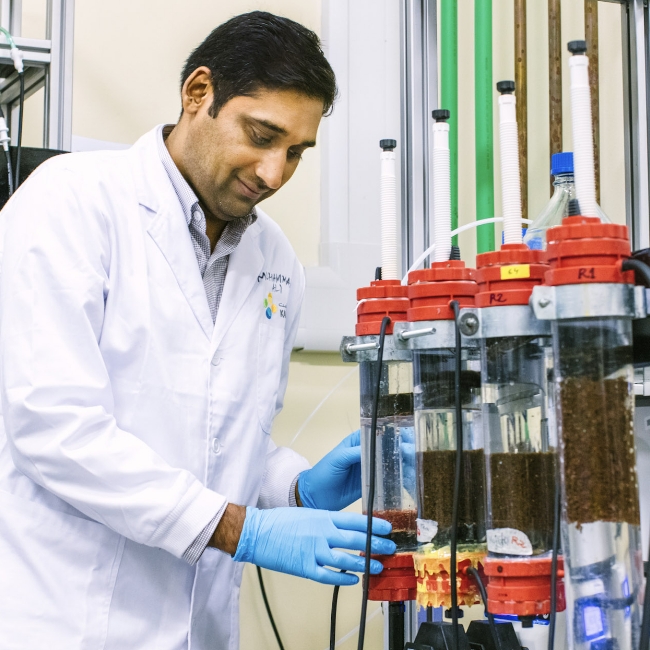
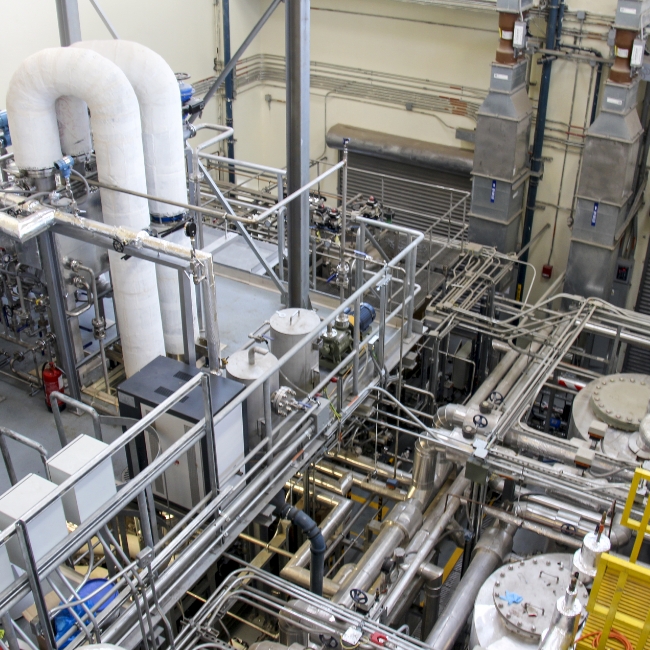


KAUST is always exploring more sustainable desalination techniques at its Water Desalination and Reuse Center. One successful example is KAUST-backed company MEDAD’s solar-powered pilot desalination installation, with hybrid cycle technology that desalinates seawater at temperatures of 60 C to 80 C using solar energy. The technology was recognized with the Sustainability Medal 2020 at the MEED Projects Awards and is currently being commissioned for use at other locations such as the Solar Village at KACST, in Riyadh.